- What is the four-layer rigid-flex board?
- The structure of the four-layer rigid-flex board
- Four-layer soft and hard board production process
- Advantages and disadvantages of four-layer rigid-flex board
- The difference between the four-layer flexible and rigid board and the four-layer reinforced flexible board
- Choose a high-quality four-layer rigid-flex board design manufacturer.
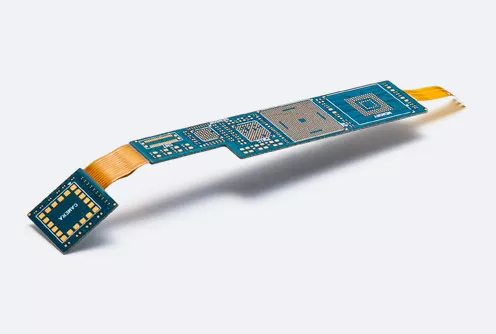
A four-layer rigid-flex board is a printed circuit board (PCB) with four layers of conductive material and is designed to be both rigid and flexible. These boards are made up of several layers of flexible and rigid PCB materials that are laminated using specialized adhesives. The conductive layers of the board are typically made of copper and are used to create the circuit pathways that connect the electronic components on the board.
Rigid-flex PCBs are used in various applications, including aerospace, military, and medical devices, where their rigidity and flexibility are beneficial. These boards are typically more complex and expensive to manufacture than traditional rigid PCBs, but their unique properties make them well-suited for applications where flexibility and durability are important.
There are several types of rigid-flex boards, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer. Single-sided rigid-flex boards have a single layer of conductive material on one side of the board, while double-sided rigid-flex boards have conductive material on both sides. Multi-layer rigid-flex boards have multiple layers of conductive material, separated by insulating material layers. The specific type of rigid-flex board used in a particular application will depend on the specific requirements of that application.
What is the four-layer rigid-flex board?
A four-layer rigid-flex board is a printed circuit board (PCB) with four layers of conductive material and is designed to be both rigid and flexible. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in various applications, including aerospace, military, and medical devices, where their rigidity and flexibility are beneficial.
The structure of the four-layer rigid-flex board
A four-layer rigid-flex board typically has four layers of conductive material laminated using specialized adhesives. These conductive layers are typically made of copper and are used to create the circuit pathways that connect the electronic components on the board. The layers are separated by layers of insulating material, which help to prevent electrical shorts and ensure the integrity of the circuit.
In a four-layer rigid-flex board, the outermost layers are typically made of a flexible PCB material, such as polyimide or polyester. These layers provide the flexibility and durability required for applications where the board will be subject to mechanical stress or movement. The inner layers of the board are typically made of a rigid PCB material, such as FR-4, which provides the structural stability and support required for the electronic components on the board.
The specific layout and design of the conductive layers on a four-layer rigid-flex board will depend on the application’s specific requirements. In general, the conductive layers are arranged in a way that maximizes the circuit’s efficiency and performance while minimizing the board’s overall size and weight. This often involves placing the power and ground layers in the inner layers of the board, with the signal layers on the outer layers.
Four-layer soft and hard board production process
The production process for a four-layer soft and hard board typically involves several steps, including circuit design, material preparation, laminate layering, drilling, and etching.
1. Circuit design: The first step in the production process is to design the circuit for the four-layer soft and hardboard. This typically involves using computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a detailed schematic of the circuit, including the placement of all electronic components and the routing of the circuit pathways.
2. Material preparation: Once the circuit design is complete, the four-layer soft and hard board materials must be prepared. This typically involves cutting the flexible and rigid PCB materials to size and preparing the copper foil for the conductive layers.
3. Laminate layering: The next step is to laminate the flexible and rigid PCB materials using specialized adhesives. This typically involves stacking the materials in the correct order and applying heat and pressure to bond them together.
4. Drilling: After the materials have been laminated, the next step is to drill holes in the board for the electronic components. This is typically done using a high-precision drill press or CNC milling machine.
5. Etching: The final step in the production process is to etch the conductive patterns onto the board using a chemical etching process. This involves applying a photoresist material to the board and exposing it to ultraviolet light to create a mask for the etching process. The board is then placed in an etching solution, which removes the exposed copper to create the desired circuit pattern.
Advantages and disadvantages of four-layer rigid-flex board
Four-layer rigid-flex boards have several advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional rigid PCBs. Some of the main advantages of four-layer rigid-flex boards include the following:
1. Increased flexibility and durability: Because they are made with flexible PCB materials, four-layer rigid-flex boards can withstand mechanical stress and movement better than traditional rigid PCBs. This makes them well-suited for applications where the board will be subjected to vibration, impact, or mechanical stress.
2. Improved circuit performance: Using multiple layers of conductive material in four-layer rigid-flex boards allows for more complex and efficient circuit designs. This can improve the circuit’s performance and reduce the board’s overall size and weight.
3. Reduced assembly costs: Because four-layer rigid-flex boards are designed to be both rigid and flexible, they can be used in applications where traditional rigid PCBs require multiple boards to be connected. This can reduce the cost and complexity of the assembly process.
Some of the main disadvantages of four-layer rigid-flex boards include the following:
1. Higher manufacturing costs: Four-layer rigid-flex boards are typically more complex and expensive than traditional rigid PCBs. This is because they require specialized equipment and materials, and the production process is generally more labor-intensive.
2. Limited design options: The use of flexible PCB materials in four-layer rigid-flex boards can limit the design options for the circuit. This is because the materials have different electrical and mechanical properties than traditional rigid PCB materials, which can impact the circuit’s performance.
3. Increased testing requirements: Because four-layer rigid-flex boards are more complex than traditional rigid PCBs, they typically require more extensive testing to ensure the integrity of the circuit. This can increase the overall cost and time required to produce the board.
The difference between the four-layer flexible and rigid board and the four-layer reinforced flexible board
The main difference between a four-layer flexible and rigid board and a four-layer reinforced flexible board is the type of materials used in their construction. A four-layer flexible and rigid board comprises layers of flexible and rigid PCB materials that are laminated using specialized adhesives. This type of board is designed to be both flexible and rigid, making it well-suited for applications where it will be subjected to mechanical stress or movement.
On the other hand, a four-layer reinforced flexible board is made up of layers of flexible PCB material that are reinforced with a rigid material, such as metal or composite. This type of board is designed to be flexible, but it has a greater degree of stiffness and support than a traditional flexible PCB. This makes it well-suited for applications where the board needs to be flexible and support heavier components or withstand higher levels of mechanical stress.
Overall, the main difference between the two types of boards is how they combine flexibility and rigidity. Four-layer flexible and rigid boards are designed to be both flexible and rigid, while four-layer reinforced flexible boards are designed to be the most flexible, with added stiffness and support.
Choose a high-quality four-layer rigid-flex board design manufacturer.
Anpllopcb is a PCB one-stop solution provider for the intelligent manufacturing of electronic products. Relying on the new thinking of the Internet, we are committed to creating a benchmark for “smart manufacturing” in the industry. We have leaped from a traditional factory to a modern digital smart manufacturing platform. Focusing on the field of electronic circuits and continuously extending the scope of services, the products cover PCB R&D and design, circuit board batch/proofing services, SMT surface mount, component procurement, and other related fields.
Be brave in innovation and dare to break through. In the future, Anpllo will use the new thinking of the Internet to build a new model of Anpllo’s intelligent manufacturing. The PCB online ordering system will be launched soon. With the support of big data and cloud computing, production and sales will be digitized. The prototype manufacturing required for supporting customer research and development will be realized and extended to mass production. The batch operation needed to create a new modern digital intelligent manufacturing layout.