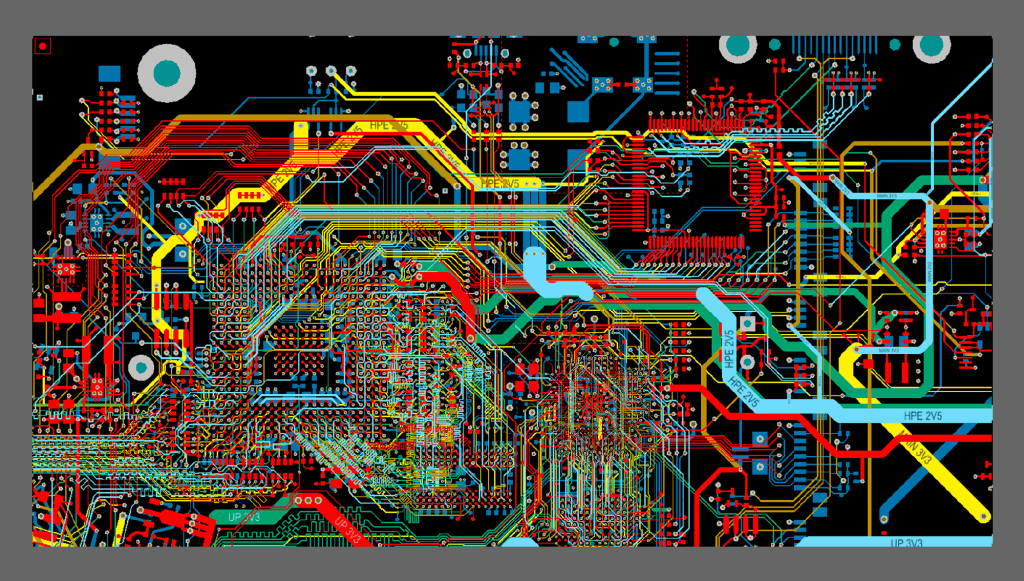
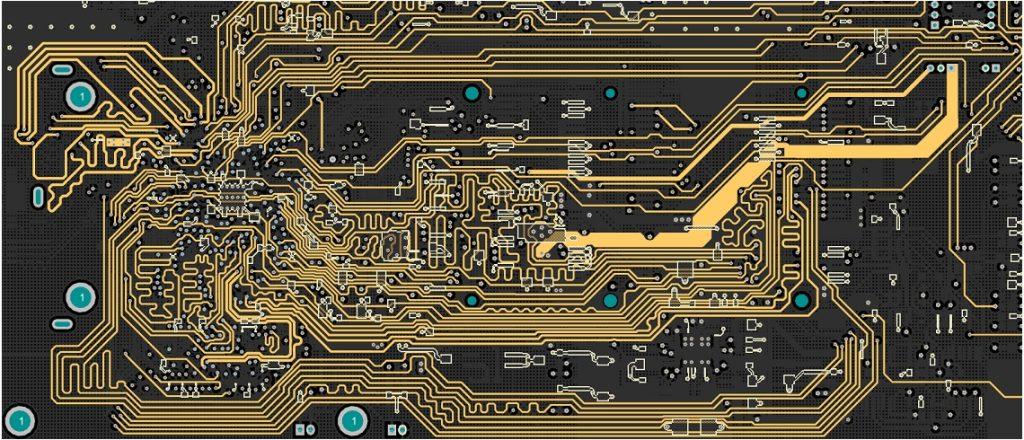
In electronic product design, PCB layout and wiring are important steps, and the good or bad PCB layout and wiring will directly affect the circuit’s performance.
Now, although there is much software to achieve automatic PCB layout routing, as the signal frequency continues to rise, many times, engineers need to understand the basic principles and techniques of PCB layout and route to make their designs flawless.
The following covers the basic principles and design techniques related to PCB layout and wiring in the form of questions and answers to difficult questions about PCB layout and wiring.
1, Q: What issues should be noted when wiring high-frequency signals?
A: Impedance matching of signal lines; spatial isolation with other signal lines; for digital high-frequency signals, differential lines will work better.
2、Q: When laying out the board, if the line is dense, the perforation may have to be more; of course, it will affect the electrical performance of the board; how to improve the electrical performance of the board?
A: For low-frequency signals, over-hole does not matter; high-frequency signals, as much as possible, reduce over-hole. Suppose more lines can consider a multilayer board.
3、Q: Are the more decoupling capacitors added to the board, the better?
A: Decoupling capacitors must be added at the right location with the right value. For example, in the power supply port of your analog devices, you need to use different capacitance values to filter out spurious signals of different frequencies.
4、Q: A good board, what is its standard?
A: A reasonable layout, power line power redundancy, high-frequency impedance, and low-frequency alignment concise.
5、Q: Through-hole and blind hole on the signal of the difference between the impact of how much? What is the principle of application?
A: The use of blind or buried holes is an effective way to improve the density of multilayer boards, reduce the number of layers and board size, and greatly reduce the number of plated through-hole. However, a through-hole is good to achieve in the process and has lower cost, so a through-hole is generally used in the design.
6、Q: When it comes to analog-digital hybrid systems, some people suggest that the electrical layer split and the ground plane takes the entire copper; others suggest that the electrical ground layer is split, different ground in the power source endpoint connection, but this is far from the return path of the signal, the specific application should be how to choose the appropriate method?
A: If you have a high-frequency > 20MHz signal line, and the length and number are more, then you need at least two layers to this analog high-frequency signal. A layer of signal lines, a layer of large area ground, and the signal line layer need to be punched enough over the hole to ground. The purpose of this is.
For analog signals, this provides a complete transmission medium and impedance matching.
The ground plane isolates the analog signal from other digital signals.
The ground loop is small enough because you hit many vias, and the ground is a large plane.
7, Q: In the circuit board, the signal input plug-in is the left edge of the PCB, MCU on the right, then the layout is placed close to the regulator power chip in the connector (power IC output 5V after a relatively long path to reach the MCU), or the power IC is placed in the middle right (power IC output 5V line to reach the MCU is relatively short, but the input power line after a relatively long (a section of the PCB)? Or is there a better layout?
A: First, is your so-called signal input plug-in an analog device? If it is an analog device, it is recommended that the layout of your power supply should try not to affect the signal integrity of the analog part. Therefore, there are several points to consider.
First, whether your voltage regulator chip is relatively clean or has a small ripple power supply, the power supply to the analog part of the power supply requirements is relatively high.
Whether the analog part and your MCU are a power supply, in a high circuit design, it is recommended to separate the power supply for the analog part and the digital part.
The power supply to the digital part needs to be considered to minimize the impact on the analog circuit part.
8, Q: In the application of high-speed signal chain, for multi-ASIC, are present analog ground and digital ground, whether to use ground split or not split ground? What are the existing guidelines? Which one works better?
A: So far, there is no definite conclusion. In general, you can consult the chip’s manual. ADI manuals for all hybrid chips recommend a grounding scheme; some recommend a common ground, and others recommend an isolated ground. This depends on the chip design.
9, Q: When to consider the line of equal length? If you want to consider the use of equal length, the difference between the length of the two signal lines can not exceed how much? How to calculate?
A: Differential line calculation ideas: If you pass a sine signal, your length difference is equal to half of its transmission wavelength, and the phase difference is 180 degrees, at which point the two signals are completely offset. So the length difference at this point is the value. And so on, the signal line difference must be less than this value.
10, Q: Is high speed in the snake alignment suitable for that situation? What are the disadvantages, such as for differential alignment, and requires two groups of signals are orthogonal?
A: Snake alignment, because of the application of different occasions and with different roles: If the snake alignment in the computer board.
If the snake alignment with the computer board, the main role of a filtering inductor and impedance matching, is to improve the circuit’s anti-interference ability. Computer motherboards in the snake alignment are mainly used in clock signals, such as PCI-Clk, AGPCIK, IDE, DIMM, and other signal lines.
If in the general ordinary PCB board, in addition to the role of filter inductor, but also as a radio antenna inductor coil and so on. Such as, a 2.4G intercom is used as an inductor.
For some signal wiring, length requirements must be strictly equal to the length of the high-speed digital PCB board to keep the delay difference between the signals in a range to ensure the effectiveness of the data read by the system in the same cycle (delay difference of more than one clock cycle will read the data of the next cycle by mistake).
For example, the hub link in the INTEL HUB architecture, with a total of 13 rods, uses a frequency of 233MHz and requires strict equal length to eliminate the hidden problem caused by time lag, and wire winding is the only solution. The delay difference is generally required to be no more than 1/4 clock cycle, and the delay difference per unit length of the line is also fixed. The delay is related to the line width, line length, copper thickness, and board layer structure. However, too long a line will increase the distributed capacitance and distributed inductance, which will degrade the signal quality.
So the clock IC pins are generally connected; ” end connection, but the snake alignment is not the role of inductance. On the contrary, the inductance will shift the signal in the rising edge of the higher harmonics phase, resulting in deterioration of signal quality, so the snake line spacing must be less than twice the line width.
The smaller the signal’s rise time, the more susceptible it is to the effects of distributed capacitance and distributed inductance.
Serpentine alignment in some special circuits plays a role in the LC filter of the distribution parameters.
11, Q: In the PCB design, how do EMC/EMI, and what specific aspects need to be considered? What measures to take?
A: A good EMI / EMC design must be considered at the beginning of the layout of the location of the device, PCB stack arrangement, the important linkage method, and the choice of devices.
For example, the location of the clock generator should be as close as possible to the external connector, high-speed signals as far as possible to go inside the layer, and pay attention to the characteristic impedance matching and reference layer to reduce reflections; the device pushed by the signal slope (slew rate) as small as possible to reduce the high-frequency components, the choice of decoupling (decoupling/bypass) capacitors to pay attention to its frequency response to meet the demand to reduce Power layer noise.
In addition, pay attention to the return path of the high-frequency signal current so that the loop area is as small as possible (that is, loop impedance as small as possible) to reduce radiation, but also the way to split the ground to control the range of high-frequency noise, the appropriate choice of PCB and shell grounding point.
12, Q: Please ask the RF broadband circuit PCB transmission line design what needs attention. How do we set the ground hole of the transmission line more appropriately, is impedance matching required to design their own or to cooperate with the PCB fabricator?
A: This issue has to consider many factors. For example, the various parameters of the PCB material, the transmission line model based on these parameters, the parameters of the device, Etc… Impedance matching generally has to be designed according to the information provided by the manufacturer.
13, Q: When the analog and digital circuits coexist, such as half of the FPGA or microcontroller digital circuit, the other half is the analog circuit part of the DAC and related amplifiers. A variety of voltage values of the power supply, encounter both digital and analog circuits to use the voltage value of the power supply, whether it is possible to use a common power supply, what are the skills in wiring and bead arrangement?
A: It is generally not recommended to use this. This will be more complex to use; it is also difficult to debug.
14, Q: Hello, please ask about the high-speed multilayer PCB design, the choice of resistors and capacitors, and other package devices; the main basis is what? Those packages are commonly used and can give a few examples.
A: 0402 is commonly used in cell phones; 0603 is commonly used in general high-speed signal modules; based on the smaller the package, the smaller the parasitic parameters; of course, different manufacturers of the same package in the high-frequency performance are very different.
It is recommended that you use special high-frequency components in key locations.
15, Q: generally, in the double panel design, is the first signal line or first ground line?
A: This should be a careful consideration. In the first consideration of the case layout, consider the alignment.
16, Q: In the design of high-speed multilayer PCB, what should pay attention to the problem? Can you do a detailed description of the solution to the problem?
A: You should pay attention to the design of your layer, that is, the signal lines, power lines, ground, and control lines, and how you are divided in each layer.
The general principle is that the analog signal and analog signal ensure at least a separate layer. The power supply is also recommended to use a separate layer.
17, Q: Please ask when the specific 2-layer board, 4-layer board, or 6-layer board is in technical terms. Is there no strict limit? (excluding volume reasons) is the frequency of the CPU or its data interaction with external devices prevailing?
A: A multilayer board can provide a complete ground plane and more signal layers, which is convenient for alignment.
The frequency of interaction should be considered for applications where the CPU will control external memory devices. If the frequency is higher, the complete ground plane must be guaranteed, and the signal lines should be kept equal in length.
18, Q: PCB cabling on the impact of analog signal transmission, how to analyze, how to distinguish between the noise introduced during signal transmission is caused by cabling or op-amp devices.
A: This is difficult to distinguish, only through PCB cabling to minimize the introduction of additional noise cabling.
19, Q: I recently learned the design of PCB; for high-speed multilayer PCB, power lines, ground, and signal lines, the line width is set to how much is appropriate; the common settings are how. Can you give an example? For example, how to set the operating frequency at 300Mhz?
A: 300MHz signal must do impedance simulation to calculate the line width and line and ground distance; power lines need to determine the line width according to the size of the current; ground in the mixed signal PCB generally does not use the “line,” but the entire plane, to ensure that the circuit resistance, and the signal line below a complete plane.
20, Q: How can the layout achieve the thermal effect?
A: There are three main aspects of heat in the PCB.
(1) the heat generated by electronic components.
(2) the heat generated by the PCB itself.
(3) heat from other parts.
In these three sources of heat, the heat generated by the components is the main source of heat, followed by the heat generated by the PCB board; the heat coming in from outside depends on the overall thermal design of the system and is not considered for the time being.
Then the purpose of thermal design is to take appropriate measures and methods to reduce the temperature of the components and PCB board temperature so that the system works properly at the right temperature. This is mainly achieved by reducing heat generation and accelerating heat dissipation.
21, Q: Can you explain the relationship between the line width and the size of the matching over-hole ratio?
A: This is a good question; it is difficult to say that there is a simple proportional relationship because the two simulations are different. One is a surface transmission one is a ring transmission. You can find impedance calculation software on the Internet and keep the impedance of the vias and transmission line impedance consistent.
22, Q: In an ordinary PCB board with an MCU control but no high-current high-speed signal requirements are not very high, then the PCB outside the perimeter of the edge of whether to lay a layer of ground to wrap the entire board will be better?
A: In general, a complete ground on the store can be.
23、Q.
(1) I know that the AD conversion chip below makes a single point of analog and digital ground connection, but if the board has more than one AD conversion chip case, how to deal with it?
(2) Does the multilayer circuit board and multiplexer switch (multiplexer) to switch the analog sampling, like the AD conversion chip, need to be separated from the analog and digital parts?
A: several ADC as far as possible together, analog ground digital ground in the ADC below the single point connection; depending on the speed of the MUX and ADC switching, the general speed of the ADC will be higher than the MUX, so it is recommended to be placed below the ADC. Of course, for insurance purposes, you can also put a magnetic bead package under the MUX, debugging depending on the specific circumstances to choose the single point of connection.
24、Q: In the conventional network circuit design, some use to connect several grounds; is there such a use? Why?
A: Not very clear about your question. For hybrid systems, there will certainly be several types of ground; always connect them at one point; the purpose of doing so is equal potential. Everyone needs a common ground level for reference.
25, Q: How effectively handle PCB in the analog and digital parts, analog ground, and digital ground?
A: Analog and digital circuits should be placed in separate areas so that the return current of the analog circuit in the analog circuit area and digital in the digital area, so that the digital will not affect the analog. Analog ground and the digital ground processing starting point are similar and can not let the return flow of digital signals to the analog ground.
26, Q: In analog and digital circuits in the PCB board design, what are the differences in the ground design? What issues need attention?
A: The main requirements of analog circuits on the ground are integrity, small loop, and impedance matching. Digital signals have no special requirements if low frequency; if the speed is high, you also need to consider impedance matching and ground integrity.
27、Q: There are generally two decoupling capacitors, 0.1 and 10; if the area is relatively tight, how to place the two capacitors? Which is better to place the back?
A: According to the specific application and for what chip to design.
28、Q: Please ask the teacher RF circuit; there are often two signals IQ; please ask whether the length of the two lines needs to be the same.
A: In the RF circuit, try to use the same.
29、Q: What is the difference between the design of high-frequency signal circuits and ordinary circuit design? Can you take the alignment design as an example and explain it briefly?
A: High-frequency circuit design to consider the impact of many parameters; in the high-frequency signal, many ordinary circuits can ignore the parameters can not be ignored, so you may want to take into account the transmission line effect.
30, Q: high-speed PCB, the wiring process over the hole avoidance, how to deal with, what is a good suggestion?
A: High-speed PCB, less perforation, by increasing the signal layer to solve the need to increase the perforation needs.
31, Q: PCB board design, how to choose the thickness of the power supply alignment? Are there any rules?
A: You can refer to: 0.15 × line width (mm) = A; you also need to consider the copper thickness.
32, Q: digital and analog circuits in the same multilayer board, analog and digital ground to be arranged on a different layer?
A: No need to do so, but the analog and digital circuits should be placed separately.
33、Q: How many holes are suitable for digital signal transmission in general? (The signal below 120Mhz)
A: Do not exceed two over-hole.
34、Q: Is the PCB board designed to avoid mutual interference problems in the circuit with analog and digital circuits?
A: Analog circuits are generally interfered with if they match reasonable radiation is very small. Interference sources from the device, power supply, space, and PCB; digital circuit due to the frequency component of many, so it is certainly a source of interference. WeChat search public number play embedded.
The solution is generally reasonable device layout, power supply, and PCB layering; if the interference characteristics of large or analog parts are very sensitive, you can consider using a shield.
35, Q: for high-speed circuit boards, there may be parasitic parameters everywhere, In the face of these parasitic parameters, we are a variety of parameters and then to eliminate, or the use of empirical methods to solve? How should we balance this efficiency and performance problem?
A: Generally speaking, we should analyze parasitic parameters’ impact on the circuit’s performance. If the impact can not be ignored, it must be considered to solve and eliminate.
36、Q: Multilayer board layout to pay attention to what matters?
A: Multilayer board layout, because the power supply and ground layer are in the inner layer, be careful not to have a suspended ground plane or power plane; in addition, to ensure that the hole hit the ground is indeed connected to the ground plane, is to add some important signal test points to facilitate the measurement of debugging.
37、Q: How to avoid high-speed signal crosstalk?
A: You can make the signal lines away from the far, avoid taking parallel lines by laying the ground or adding protection to play a shielding role, and so on.
38、Q: Please ask in the design of multilayer board often use the power plane, but in the double-layer board need to design the power plane?
A: It is not easy because you have a variety of signal lines in the double-layer layout has been about the same.
39, Q: PCB board thickness has any effect on the circuit? How is it generally selected?
A: The thickness is more important in impedance matching; PCB manufacturers will ask if impedance matching is calculated when the board thickness is how much; PCB manufacturers will be made according to your requirements.
40、Q: The ground plane can make the signal loop, and the signal line will produce parasitic capacitance; how should this trade-off?
A: It depends on whether the parasitic capacitance of the signal has a non-negligible impact. If it is not negligible, it should be reconsidered.
41, Q: LDO output as a digital or analog power supply means the digital and analog connection to the power output is good?
A: If you want to use an LDO to provide power for digital and analog, it is recommended that the analog power supply first, analog power after LC filtering, for the digital power supply.
42、Q: Should I use a magnetic bead between analog Vcc and digital Vcc, or should I use a magnetic bead between analog ground and digital ground?
A: Analog VCC is filtered by LC to get digital VCC, and a magnetic bead is used between analog ground and digital ground.
43、Q: How to wire differential signal lines such as LVDS?
A: Generally need to pay attention to all wiring, including the placement of surrounding devices; the ground plane needs to be symmetrical.
44、Q: For a good PCB design, you need to do their own as little as possible to the outside of the emission of electromagnetic radiation, but also to prevent external electromagnetic radiation to their interference; please ask to prevent external electromagnetic interference, the circuit needs to take what measures?
A: The method is shielding to prevent external interference from entering. Circuit, such as when there is INA, must add an RFI filter before the INA to filter out RF interference.
45, Q: the use of high clock frequency fast integrated circuit chip circuit, how to solve the problem of transmission line effect when the PCB board design?
A: This fast integrated circuit chip is what chip? If it is a digital chip, generally do not have to consider it.
If it is an analog chip, see whether the transmission line effect is large enough to affect its performance.
46, Q: Is it still necessary to cover copper in a multilayer PCB design? If the copper should be connected to which layer?
A: The top and bottom layers cannot lay copper, if there is a complete internal ground plane and power plane.
47, Q: In high-speed multilayer PCB design, impedance simulation is generally how to carry out using what software? Is there any special attention to the problem?
A: You can use Multisim software to simulate the resistor-capacitor effect.
48、Q: Some devices have thin pins, but the PCB board alignment is thicker, will cause an impedance mismatch after connection? If there is, how to solve it?
A: It depends on what the device is. Moreover, the device impedance is generally given in the datasheet, and the pin thickness is irrelevant.
49, Q: differential lines generally need to be equal in length if it is really difficult to achieve in the LAYOUT, are there other remedial measures?
A: You can go through the snake line to solve the problem of equal length, and now most of the PCB software can automatically go equal length line; it is very convenient.
50, Q: in the chip with a multimeter to measure the analog ground and digital ground interface so that the digital ground’s analog region is not a multi-point connection?
A: The internal ground pins of the chip are connected. However, it still needs to be connected to the PCB board. The ideal single ground point should understand the chip’s internal analog and digital part of the connection point location. The PCB board single point of connection location is also designed in the chip’s analog and digital demarcation points.
51, Q: Due to the limitations of the size of the board, my circuit board uses two sides of the SMD solder chip; the board goes much over-hole, and the signal lines also go in the vicinity so that the alignment of the signal will produce interference?
A: If it is a low-speed digital signal, it should not be a big problem. Otherwise, it will certainly affect the quality of the signal.
52, Q: digital line in considering whether to do impedance matching is to see the signal out to reflect; the total time is more than 20% of the rising edge if more than the impedance matching. Do you want to impedance match the analog line? How to consider it?
A: Low-frequency analog signals do not need to match; RF analog signals should also consider the matching problem.
53、Q: About the complete ground plane, in the use of AD/DA chipboard, if the number of layers is more, it can provide a complete analog ground and a complete digital ground; it can also be divided into analog ground and digital ground on both layers of the ground plane. Which of the two is better or worse?
A: Generally speaking, the complete ground plane will be laid. Unless there are some special cases, such as the analog part of the board and the digital part being separated, they can be easily distinguished.
54、Q: When connecting digital and analog ground with magnetic beads or MECCA, it uses its frequency characteristics so that the high-frequency components in the digital ground do not affect the analog ground while ensuring that the level of the two is equal. So, 0ohm resistor connected to digital, analog ground, what role, and sometimes only a small piece of copper connection, can you analyze?
A: The equivalent circuit of the magnetic beads is equivalent to a band resistance limiter, which only has a significant suppression effect on the noise at a certain frequency point, and it is necessary to estimate the frequency of the noise point in advance when using it in order to choose the appropriate model. For frequency uncertainty or unpredictable cases, the beads do not fit. The 0-ohm resistor is equivalent to a very narrow current path, which can effectively limit the loop current so that the noise is suppressed. The resistor has an attenuation effect in all frequency bands (0ohm resistor also has impedance), which is stronger than magnetic beads. Copper skin is similar to 0ohm resistors.)
55、Q: How to avoid the noise introduced during wiring?
A: Digital ground and analog ground to a single point of grounding; otherwise, the digital ground return current will flow through the analog ground on the analog circuit to cause interference.
56, Q: PCB, how to prevent PWM and other sudden changes in the signal to the analog signal (such as op-amp) generated interference, and how to test the size of this interference (radiation interference or conducted interference)? In addition to the layout of the wiring needing attention, there are no other methods to suppress (in addition to the means of shielding).
A: To start from several interfaces of the op-amp, the input side prevents spatial coupling interference and PCB crosstalk (layout improvement); the power supply requires different capacitance decoupling capacitors. The test can use an oscilloscope probe to test the location mentioned above to determine where the interference comes from.
PWM signal if the low-pass filtering into DC control voltage, you can consider doing filtering, or parallel to ground a small capacitor, so that the PWM waveform becomes rounded, reducing the high-frequency component.
57, Q: Please ask, in the board, an ARM or FPGA will often be connected to the outside of many RAM, FLASH such devices, please ask these main chips and these memories need to pay attention to what is connected between the number of holes, what is the limit? What is the common size of vias in digital signals? Does the size of the vias have a significant impact on the signal?
A: If the speed is greater than 100MHz, a signal line should not be more than two holes; the hole can not be too small; in general, a 10 mil aperture can be.
58, Q: please ask in the double cloth panel (high frequency), the top ground and the bottom ground connected to the hole is also the less, the better? Then how to put the hole more reasonable?
A: Fewer holes are for signal lines; if it is the ground of the hole, more appropriate will reduce the ground loop and impedance. The principle is to put in the device.
59、Q: What should I pay attention to when wiring LVDS signals? How to wire it?
A: Parallel and equal length;
60、Q: Is the parallel wiring of data lines for mutual interference?
A: To prevent crosstalk, parallel lines should pay attention to the line-to-line spacing.
61、Q: In a 4-layer board, cloth has a whole acquisition system, analog amplification, digital acquisition, and MCU. Cloth, how to measure the input impedance of this system, how to do the system input impedance and sensor matching, how to match? There are no relevant design principles.
A: I don’t know how high the frequency of your analog signal is; if it is not high, then impedance matching is unnecessary. Impedance matching can use simulation software to calculate the impedance of the PCB. For example, in AppCAD, the device’s impedance can be checked through the manual.
62, Q: I often see many ground holes on the PCB board; the more ground holes, the better. Are there any rules?
A: No. To minimize the use of an over-hole, in the case of having to use an over-hole, also consider reducing the impact of the over-hole on the circuit.
63、Q: Inevitably, there will be a cross-plane when wiring multilayer boards. Our everyday cooking is to prioritize the differential lines when cutting the plane without crossing the plane. However, some teachers think that the single end can not cross, and the differential is not so strict. Please ask the teacher’s opinion on this.
A: single-ended and differential signals across the ground plane have to go back if the return flow around a large circle goes back, as well as induction of more interference in, if the same noise on the differential line, it will cancel each other out, so there is some truth to it.
64, Q: How to distinguish between digital and analog ground in the high-speed multilayer PCB design? Is it connected according to the device data sheet?
A: High-speed design does not have to be divided into the digital and analog ground.
65, Q: How to consider the fusing current of the PCB alignment? PCB alignment, how much current will fuse, and what factors are related?
A: Reference 0.15 × line width (mm) = A, which is the current. Design time can not use the fusing current to do the budget. This is the cross-sectional area of the copper wire.
66、Q: What protection is needed in the signal input and output interface and power input interface, Etc.? When the power supply is 220V input to DC, what protective measures need to be taken in the actual application?
A: TVS tube, fuse these in the power supply is necessary. Depending on the situation, you must add TVS tubes and diodes to protect the analog circuit input from a large voltage.
67, Q: PCB board wiring bending 45-degree angle and rounded two, what are the advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose?
A: From the perspective of impedance matching, both lines can be made to match the corner of the bend. However, the rounded corners may not be good processing.
68、Q: In the high-frequency alignment, if the size is limited, what are the common or reasonable alignment methods? For example, snake alignment, can it?
A: Not good; it will introduce more parasitic parameters.
69、Q: Please ask the key input model when using the instrumentation amplifier; I still need copper cladding around its device layer; I have copper cladding on the bottom layer. For an instrumentation amplifier feedback resistor, I am using a straight plug; the lead is long, replaced by a chip resistor temperature drift, and will not meet the requirements; how should I deal with it?
A: The general instrumentation amplifier chip data will have the recommended Layout method and diagram, which you can refer to. Ensuring that the lead is short and thick is a must. The choice of the chip with low resistance or direct plugging with high resistance is good; it depends on the specific debugging results.
70, Q: PCB software can be automatically wired, but the location of the device layout is not to be placed manually.
A: Layout wiring is done manually.
71, Q: When making PCB boards, are there no special provisions or general how to select materials? I am now in the production of the high-frequency signal circuit board; please ask you to choose what material PCB board is better.
A: The current high-frequency circuit board substrate is more often fluorine than the dielectric substrate, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), usually called Teflon, used in more than 5GHz. Do the board with the PCB manufacturer can explain?
72, Q: I am a beginner in PCB design; I would like to understand the selection rules for decoupling capacitors is what? Moreover, the value of the size of how to calculate?
A: In general, for the power supply part, use 10u and 0.1u capacitor decoupling to consider both high-frequency and low-frequency decoupling; for other original components, generally use 0.1u capacitor in the power supply part decoupling.
73、Q: How much attenuation can be achieved by a 5khz pulse signal on the board after going 20cm long, 10mil wide alignment?
A: Different materials of the PCB parasitic parameters are different; you can build a model to calculate the parasitic parameters used.
74, Q: in the high-frequency microstrip line alignment and the distance between the ground plane have any requirements? For example, greater than 1mm. or not much requirement, as long as almost can? Or should it be calculated by a coplanar waveguide?
A: Must be calculated using a coplanar waveguide or microstrip line impedance simulation.
75、Q: How to wire to minimize the crosstalk between lines of high-frequency signals?
A: A good match of high-frequency signals will reduce reflections and radiation.
76, Q: I would like to ask in DC-DCConvertIC, in the IC below, the need to connect to the ground plane, through Via connected to the ground plane, Via hole number, and the degree of influence why?
A: Generally, the design can be based on the reference design. Due to the larger current, we may need a certain number of Via.
77、Q: impedance matching, if the impedance value given by the pin is complex, that is, both the impedance part and reactance part, how to do impedance matching at this time? Consider the resistive part alone.
A: Consider conjugate matching, the imaginary part of the impedance will be offset.
78、Q: What kind of concentrated and distributed parameters are better in high frequency? How do you choose these two methods more appropriately?
A: The distribution method is higher but more complex; the set whole way is relatively simplified, but there is a certain error.
79, Q: double-layer board connected to the upper and lower copper cladding ground. What is the requirement for the distribution of the perforation?
A: Generally speaking, there should not be too many requirements to improve connectivity.
80、Q: How to balance the amplifier input’s inductance and parasitic capacitance in an IF application?
A: Generally speaking, the impact of parasitic inductance and capacitance on the IF circuit is small and can be ignored. Just make sure not to introduce large parasitic capacitance and inductance values.
81、Q: How to effectively reduce the impact of interference between circuit components, and how to layout the amplifier to limit the introduction of ripple suppression?
Answer.
① The principles of reducing interference are: reduce the radiation end; strengthen the isolation, shielding, and decoupling of the interfered.
② The principles of ripple reduction are also: reduce the ripple output of switching power supply; sufficient decoupling filtering.
82, Q: 6-layer design, layer allocation techniques, those alignments to the middle layer?
A: It depends on your design. The principle is to ensure that the analog signal lines and analog ground have two separate layers.
83, Q: in the analog ground and digital ground connected, the method used in the digital ground to connect a suitable bead to the analog ground? How to choose this bead?
A: The magnetic beads mainly isolate high-frequency noise; different beads’ filter frequency is different, so according to the noise on the board, choose the right device.
84、Q: What do you want to pay attention to for the layout of the signal higher than 5G?
A: Both to consider the transmission line effect, but also to consider the parasitic effect and EMI problems.
85、Q: circuit with high-speed logic devices, wiring length for how long?
A: Wiring is not afraid of long, asymmetry, or a relatively large difference, which is easy because of the time delay caused by the wrong logic.
86, Q: In the high-speed digital circuit board, there are multiple power supplies of different voltage values; laying power planes should try to use multiple power planes, or are the same layer of power planes arranged separately?
A: You can have multiple voltages on a plane; pay attention to separating them. You can also take a separate layer of important power supply to ensure that it is not interfered with by other power supplies.
87, Q: in the walk differential line, due to space constraints, it can not be completely mid and equal length; please ask is an equidistant priority or equal length priority.
A: Equal length can ensure impedance matching, but not equally spaced, which impacts the differential matching and the need for simulation testing.
88、Q: In the PCB layout, how to reduce electromagnetic interference? In addition which modules should be closer to the main control chip?
A: For the main controller, the main transmission of digital signals, so the analog and power parts should be far from the controller; To reduce electromagnetic interference, you need to pay attention to matching, decoupling, layout wiring, layering, and other issues, it is recommended to refer to some information.
89、Q: When considering the signal integrity, if only know the frequency of the digital chip is 1GHZ, generally will estimate his rise time is 1/10 of the cycle, that is, 0.1ns. Any basis?
A: This is a general principle; the speed depends on the speed of the device output port. If too slow will affect the verdict. Faster, the chip process can not reach.
90, Q: Hello, please ask the ARM chip to improve the anti-interference power supply in addition to accessing the power input TVS tube; the input pin of the power input to connect the inductor is better, or are magnetic beads better?
A: Generally will use magnetic beads.
91, Q: PCB board online can be simulated; that is, how to verify that the board has no problems?
A: Some PCB software, such as cadence, can do alignment checks and integrity analysis.
92, Q: in the PCB wiring, some people in the signal input and output string a resistor for termination, Is this role? How to choose this resistor? What places need to do so?
A: It depends on the role of the series resistor; some are to play the role of current limiting, and some may do impedance matching.
93, Q: What is a good suppression program for high-speed bursts affecting the power supply or a more systematic way of dealing with it?
A: What you call high-speed bursts is nothing more than interference signals of different frequencies, using different values of capacitance retirement couples.
94、Q: What are the special requirements for high-speed PCB plates?
A: High-frequency circuits have requirements for PCB materials. In the high frequency, consider the transmission line effect.
95, Q: Please make a point of introduction and practice the impedance of the signal line matching.
A: The lower frequency occasions, the need to consider the relationship between the width of the signal line and the carrying capacity of the current; high frequency, the need to consider matching the length of the problem.
96, Q: What are the anti-interference measures for high-frequency signal lines? Wiring should pay attention to what aspects?
A: This issue is relatively broad; it is difficult to say in a sentence or two.
97, Q: why high-speed signals do not need to be divided into the digital and analog ground?
A: Because the driver side can adjust the output phase difference and PCB layout and then adjusting it is difficult, the receiver side of the direct input can not be adjusted.
98, Q: on the differential line of equal length compensation, why do you directly recommend compensation on the driver’s side? EricBogatin’s book also only gives the conclusion but no explanation.
A: Some chips on the driver side have an adjustment function, the PCB line design is not easy to change, and the receiver side of the direct input generally has no delay adjustment function.
99, Q: in the high-frequency selection of board materials, the dielectric constant is not the smaller, the better?
A: It means that the parasitic capacitance is small; however, for the design of the signal line, the characteristic impedance of the dielectric constant is required and can not be generalized.
100, Q: What frequency crystal should the MCU and the crystal alignment be considered?
A: The crystal and MCU should be as close as possible, with a short linear connection.
101, Q: switching power supply over the DC power with about 100mv noise, how should it be effectively filtered?
A: You can consider adding modulator LDO products to stabilize the power supply or consider the appropriate decoupling capacitors to filter out the ripple.
102, Q: analog power supply can also lay the plane, whether and the role of the same ground?
A: The power supply can certainly lay flat. If you can not lay the plane, the power line should be as thick as possible.
103, Q: please ask, two-layer circuit board copper, when to choose both sides are covered, when to choose only one side of the copper cover it?
A: If you can ensure that one side is a full ground plane, you can lay only one layer.
104, Q: Please ask, in the design of a high-frequency (1GHz or more) board, what are the requirements for the size of the vias and vias spacing? What are the factors that need to be taken into account when matching the impedance? Do I need to pay attention to the board material? What are the considerations for the distance between differential alignment and ground plane?
A: Considering the above indicators, it is recommended to do the overall circuit simulation and debug parasitic effects that will affect the simulation effect, the need for repeated verification, and experimentation.