- Introduction to the traditional PCB assembly process
- Through-Hole Technology Assembly (THT): An overview of the steps involved
- The PCBA steps followed in SMT assembly are as follows.
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is more efficient in the complex PCB assembly process.
- SMT assembly vs. THT assembly
- Contact Us
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are at the heart of every electronic device we connect today. These PCBs interconnect electronic components by creating a conductive path through copper solder pads and connecting wires. PCB assembly is the process of producing printed circuit boards. It is a manufacturing technique that transforms raw materials into PCB motherboards for electronic products. It is used in many industries, including military and aerospace. This type of manufacturing requires skilled professionals to lay out the design and assemble it. As a result, the PCB assembly process has become one of the most interesting concepts in electronics. This article describes the different types of PCB assembly types and processes and provides professional insights.
Introduction to the traditional PCB assembly process
The basic PCB assembly (often called PCBA) is performed in the following manner.
(1) Solder paste application: Solder paste particles mixed with flux are applied to the PCB’s backplane. Stencils of different sizes and shapes are used to ensure that the paste is applied only at specific locations.
(2) Component placement: Placement of small electronic components of the circuit on the solder paste board manually or automatically with the help of a pick-and-place automatic mechanism.
(3) Reflow: The solder paste curing occurs during the reflow process. The PCB board with the installed components is passed through a reflow oven with a temperature exceeding 500°F. After the solder paste melts, it is returned to the conveyor and cured by exposing it to the cooler.
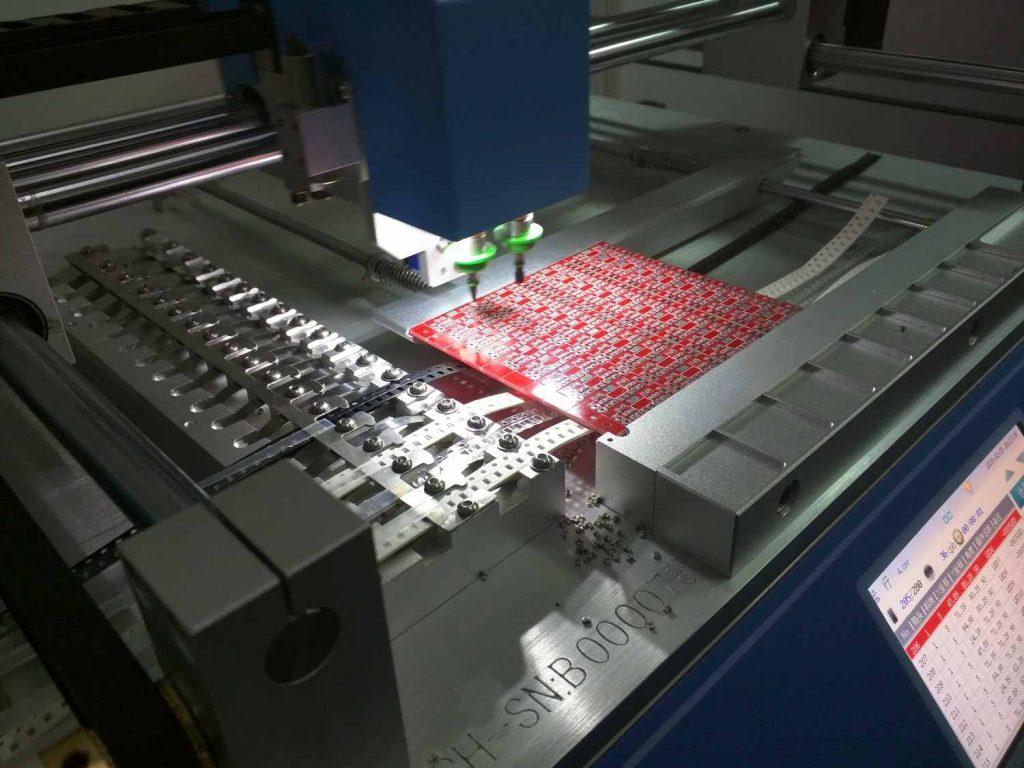

(4) Inspection: This is done after reflow. An inspection is performed to check the functionality of the component. This stage is important because it helps to identify misplaced components, poor-quality connections, and shorts. Usually, misplacement occurs during the reflow process. PCB manufacturers use manual, X-ray, and automated optical inspection at this stage.
(5) Through-hole parts insertion: Many boards require the insertion of both through-hole and surface-mounted components. Therefore, it is completed in this step. Usually, through-hole insertion is performed using wave soldering or manual soldering.
(6) Final inspection and cleaning: The PCB is checked for electrical potential by testing it at different currents and voltages. Once the PCB board passes this inspection stage, it is cleaned with deionized water, as soldering leaves some residue. After washing, they are dried under compressed air and packaged beautifully.
This is the traditional PCB assembly process followed. The figure shows that most PCBs are assembled using through-hole technology (THT), surface mount technology assembly (SMT), and hybrid assembly processes. These PCBA processes are discussed further.
Through-Hole Technology Assembly (THT): An overview of the steps involved
Through-Hole Technology (THT) differs in only a few steps of PCBA. Let us discuss the steps of THA for PCBA.
① Component Placement: In this process, experienced engineers manually install the components. The installation process of manually picking and placing components requires maximum precision and speed to ensure component placement. Engineers should follow THT standards and regulations for optimal functionality.
② Inspection and Component Alignment: The PCB board is matched to the design shipping frame to ensure accurate placement of components. If any misallocation of components is found, correct only then. Calibration is easier before soldering, so component placement is corrected at this stage.
③ Wave Soldering: In THT, wave soldering is performed to cure the solder paste and keep the component intact in its specific location. In wave soldering, the PCB board with the components mounted moves above the slow-moving liquid solder which is heated at a temperature of 500°F or more. It is then exposed to a cooler to cure the connections.
Surface Mount Technology Assembly (SMT): The Different Steps Involved
The PCBA steps followed in SMT assembly are as follows.
(1) Solder paste application/printing: Referring to the design template, the solder paste is applied to the board via a solder paste printer. This ensures that the solder paste is printed satisfactorily at specific locations.
(2) Component placement: Component placement is automatic in SMT assemblies. The board is sent from the printer to the component mounting rack, which is picked up and placed by an automatic mechanical pick-and-place mechanism. This technique saves time compared to manual processes and ensures the precise placement of specific components.
(3) Reflow Soldering: After component mounting, the PCB is placed in a furnace where solder paste is melted and deposited around the component. The PCB passes through a cooler to hold the component in place.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is more efficient in the complex PCB assembly process.
Because of the increasing complexity of electronic devices and PCB designs, hybrid assembly types are also used in the industry. Although, as the name implies, the hybrid PCB assembly process merges THT and SMT.
While surface mount technology has become the primary mounting method in PCB manufacturing, some components are still unsuitable for SMT assembly. Then SMT assembly and THT assembly must be applied on the same board. This combination of techniques is called a hybrid assembly and does not use solder paste in the manufacturing process.
Most components are soldered to the board in a surface mount configuration, but for some components not available in SMT production, hybrid PCBA assembly is required.
SMT assembly vs. THT assembly
1. SMT components are soldered to the board via a reflow machine, and the process is fully automated. Whereas THT assembly requires pre-drilling holes in the board and using leads to connect components and circuits, wave soldering and hand soldering are both conventional methods in the THT assembly process.
2. PCBs with surface mount devices (SMD) can be reflow or wave soldered, but PCBs with through-hole components can only be wave soldered. Therefore, if both SMT and THT components are used on the board, there are more steps in the assembly process. Usually, the SMT process is performed first, followed by THT assembly.
3. Advanced and precise machines enable SMT assembly with high precision and speed. Those small and thin components can be placed precisely on the board, making SMT more suitable for high-density and small-size PCB applications. Moreover, THT is more popular for those components with large sizes and high-reliability requirements, as it provides stronger connections than SMT components.
In summary, SMT placement plants offer high productivity, high accuracy, lightweight, and low cost. SMT is more economical and faster for mass production. THT components are typically highly reliable, highly stress-resistant, heavier, and more expensive. THT is the assembly method for low-volume PCB and prototype manufacturing.
Contact Us
We offer complete Turn-Key and partial Turn-Key board assembly services. We specialize in rigid and flexible PCB assembly. In Full Turn-Key PCB, we handle everything from fabricating the board, ordering the components, online order tracking, quality checking, and final assembly.
Anpllopcb assembly services include instant online printed circuit board quotes and turnkey jobs completed in five days or less.
Our fast-printed circuit board (PCBA) assembly service. We can assemble PCBs with surface mount (SMT), through-hole (THT), and composite components at an affordable price.
Anpllopcb specializes in building your short-run, one-off, and prototype PCB assemblies with fast turnaround times and instant online quoting and ordering. PCB assembly specialists. From one-off prototypes to low-volume production to fill orders.