- 1.PCB layout
- 2.PCB wiring
- (1) PCB wiring priorities
- (2) four specific PCB wiring way
- (3) PCB wiring common rules
- 1, the direction of PCB wiring control rules.
- 2, PCB alignment of the open-loop inspection rules.
- 3, PCB impedance matching check rules.
- 4, the alignment length control rules.
- 5, chamfering rules.
- 6, device decoupling rules.
- 7. PCB device layout partitioning/layering rules.
- 8. Ground loop rules.
- 9, the integrity of the power and ground layer rules.
- 10, 3W rule.
- 11、Shield protection
- 12, alignment termination network rules.
- 13, pcb alignment closed-loop inspection rules.
- 14, PCB alignment of the branch length control rules.
- 15, PCB alignment of the resonance rules.
- 16, isolated copper zone control rules.
- 17, overlapping power and ground layer rules.
- 18, 20H rule.
- (4) Other
- Summary
1.PCB layout
PCB components layout of the 10 rules:
1. PCB layout follows the “first big, then small, first difficult, then easy” layout principle; that is, the important unit circuit, the core components should be prioritized layout.
2. PCB layout should refer to the schematic diagram according to the main component’s main signal flow pattern of the single board arrangement.
3. PCB on the arrangement of components to facilitate debugging and maintenance, that is, small components around the large components can not be placed, the need to debug elements, devices around the sufficient space.
4. the same structure circuit parts, as far as possible, using the “symmetrical” standard layout.
5. by the uniform distribution, balance of gravity, and the PCB standard optimization layout.
6. the same cartridge components in the X or Y direction should be placed in one direction. The same type of polarized discrete components should also strive to maintain consistency in the X or Y direction to facilitate the production and inspection of PCB boards.
7. PCB layout on the heat-generating components should generally be evenly distributed to facilitate the heat dissipation of the single board and the whole machine, in addition to temperature detection components other than temperature-sensitive devices should be far away from the components that generate a lot of heat.
8. PCB layout should try to meet the following requirements: the total connection as short as possible, the shortest key signal lines; high voltage, high current signal and small current, low voltage weak signal completely separate; analogue signal and digital signal separate; high-frequency signal and low-frequency signal separate; high-frequency components of the interval to be adequate.
9, PCB decoupling capacitor layout should be as close as possible to the IC power supply pins and make the shortest circuit between the power supply and ground.
10, PCB component layout, due consideration should be given to using the same power supply devices as far as possible to facilitate future power separation.
2.PCB wiring
(1) PCB wiring priorities
Key signal line priority: fancy small signals, high-speed signals, clock signals and synchronization signals and other key signal priority wiring
Density priority principle: start wiring from the most complex devices connected on the PCB single board. Start wiring from the most densely connected area on the PCB board.
Points to note:
a. Try to provide a special wiring layer for key signals such as clock signals, high-frequency signals, sensitive signals, etc., and ensure their minimum loop area. Manual priority wiring, shielding and increased safety spacing should be adopted if necessary. Ensure signal quality.
b. The EMC environment between the power and ground layers is poor, and the arrangement of signals sensitive to interference should be avoided.
c. Networks with impedance control requirements should be wired according to line length and width requirements as far as possible.
(2) four specific PCB wiring way
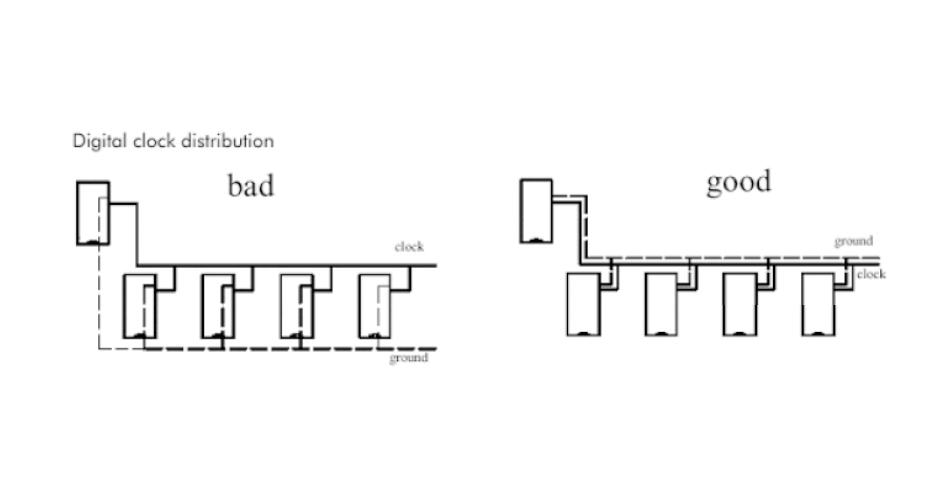
1, the clock wiring.
The clock line is one of the factors impacting EMC’s greatest impact. The clock line should be less perforated, avoid other signal lines and walk the line, and be far away from the general signal lines to avoid interference with the signal lines. At the same time, the board should avoid the power part to prevent power and clock interference from each other.
If the board has a special clock generation chip, the bottom of the line can not be walked; if necessary, it should be laid below the copper and can also be dedicated to its ground cut. Many chips reference the crystal oscillator; these crystals below should not be wired; lay copper isolation.
2, right-angle alignment:
Right-angle alignment is generally required in PCB wiring to avoid the situation, but also almost becomes a measure of PCB wiring, good or bad, one of the criteria. The right-angle alignment will have how much impact on the signal transmission? In principle, right-angle alignment will change the transmission line width, resulting in discontinuity of impedance. The right angle alignment and the corner sharp angle alignment may also cause impedance changes.
The right-angle alignment of the impact on the signal is mainly reflected in three areas.
(1) the corner can be equivalent to the capacitive load on the transmission line, slowing the rise time.
(2) impedance discontinuity can cause the reflection of the signal.
(3) is the EMI generated by the right angle tip.
3, differential alignment :
See: Altium Designer — differential distribution lines and impedance matching
A differential signal (Differential Signal) in high-speed PCB circuit design is increasingly widely used; the circuit of the most critical signal often has to use a differential structure design. Definition: In layman’s terms, the driver sends two equal and opposite signals, and the receiver determines the logic state “0” or “1” by comparing the difference between the two voltages. The pair of lines carrying the differential signal is called differential lines.
Differential and ordinary single-ended signals compared to the alignment, the most obvious advantages are reflected in the following three aspects:
a. Anti-interference ability, because the coupling between the two differential alignments is very good when the external noise interference is almost simultaneously coupled to the two lines, and the receiving end is concerned only about the difference between the two signals so that the external common-mode noise can be completely offset.
b. Can effectively suppress EMI, the same reason, due to the opposite polarity of the two signals, their external radiation of electromagnetic fields can cancel each other out; the closer the coupling, the less electromagnetic energy leaked to the outside world.
c. Precise timing positioning, because the switching change of the differential signal is located at the intersection of the two signals, unlike ordinary single-ended signals that rely on high and low threshold voltages, and is, therefore, less affected by process and temperature, reducing timing errors and making it more suitable for low-amplitude signal circuits. The current popular LVDS (low voltage differential signalling) refers to this small amplitude differential signalling technology.
PCB design engineers are the most concerned about ensuring that the actual alignment can fully play these advantages of differential alignment. Perhaps as long as they are exposed to the PCB layout wiring, people will understand the general requirements of the differential alignment, that is, “equal length, equal distance”.
The equal length ensures that the two differential signals maintain the opposite polarity, reducing the common mode component; isometric mainly ensures that the two differential impedance is consistent, reducing reflections. “As close as possible to the principle” is sometimes one of the requirements of differential alignment.
4, snake line:
Snake line is a PCB layout wiring design that is often used in a class of alignment. The main purpose is to adjust the delay to meet the system timing design requirements. PCB designers should understand that the snake line will destroy the signal quality and change the transmission delay and PCB wiring to avoid use. But the actual PCB design often has to deliberately wind the line to ensure that the signal has sufficient hold time or to reduce the time offset between the same group of signals.
Points to note:
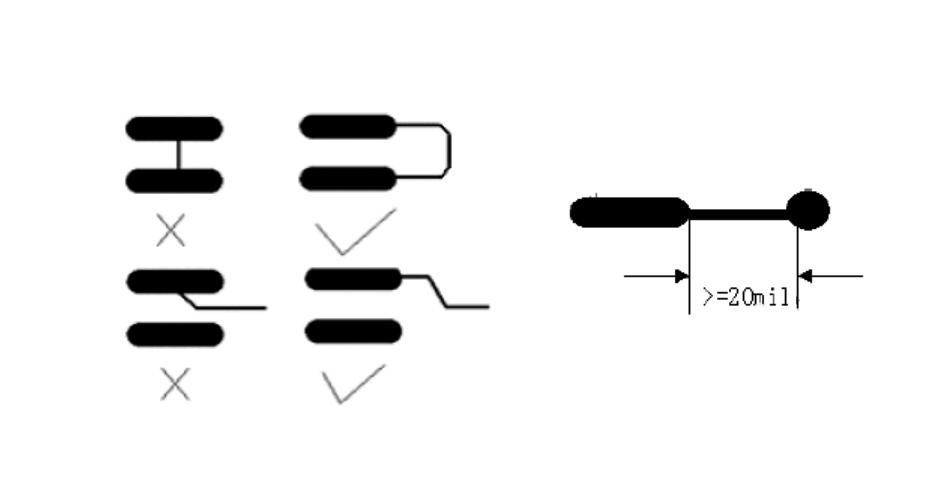
Pairs of differential signal lines, the general parallel alignment, as little as possible to punch holes, must be punched, should be two lines together to achieve impedance matching.
The same properties of a group of buses should try to parallel alignment, to do as much as possible equal length. From the SMD pads lead to the overhaul as far away from the pad.
(3) PCB wiring common rules
1, the direction of PCB wiring control rules.
That is the direction of adjacent alignment layers into an orthogonal structure. Avoid different signal lines in adjacent layers in the same direction to reduce unnecessary interlayer tampering; when the board structure constraints (such as some backplane) are difficult to avoid the situation, especially when the signal rate is high, should consider the ground plane isolation of the wiring layer, the ground signal line isolation of the signal lines.
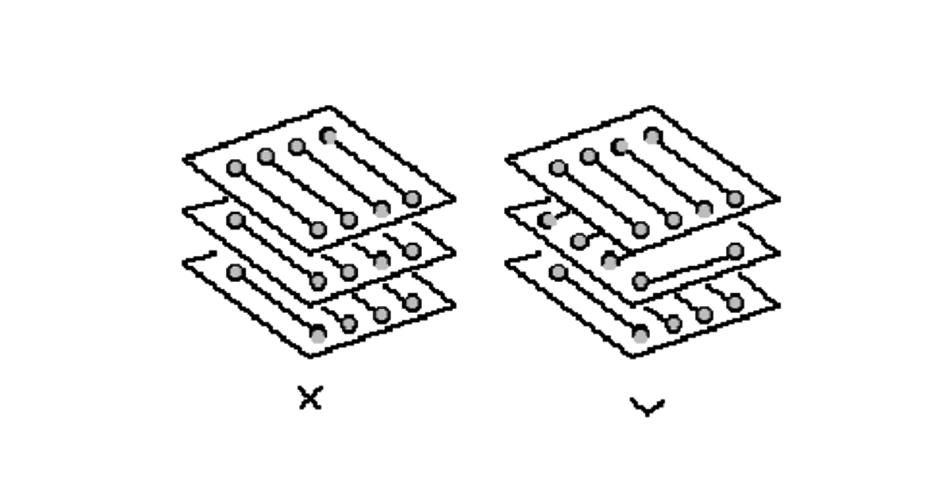
2, PCB alignment of the open-loop inspection rules.
Generally, do not allow one end of the floating PCB wiring (Dangling Line) to avoid the “antenna effect” and reduce unnecessary interference radiation and acceptance. Otherwise, it may bring unpredictable results.
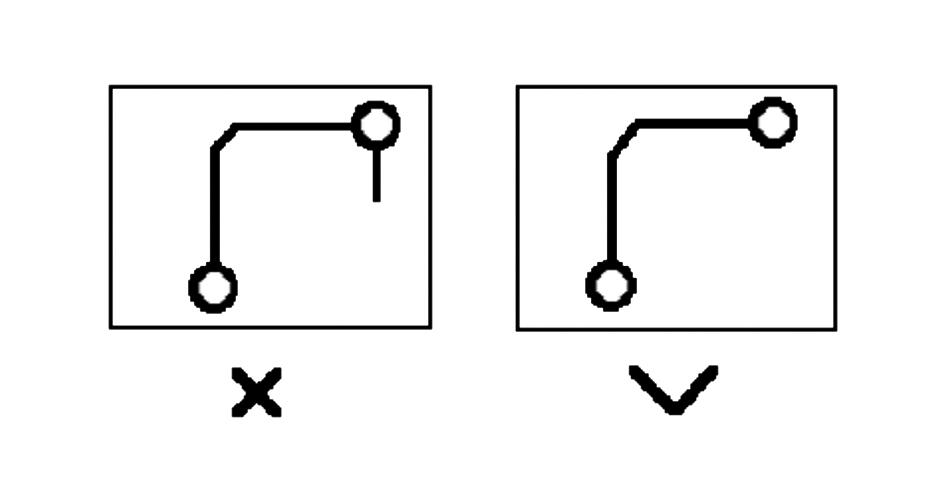
3, PCB impedance matching check rules.
The same network of PCB wiring width should be consistent; PCB line width changes will cause the line characteristics of the impedance to be not uniform; when the transmission speed is higher will produce reflections, in the PCB design should try to avoid this situation. In some conditions, such as plug-in lead-in line, BGA package lead-in line similar structure, may not be able to avoid the change in line width, should try to reduce the effective length of the middle inconsistent part.
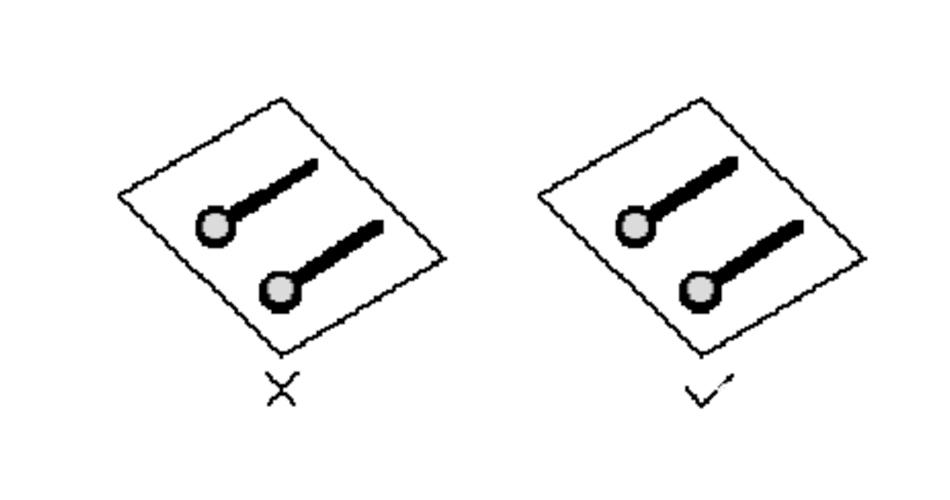
4, the alignment length control rules.
That is, the rule of short lines, in the PCB design, should try to make the wiring length as short as possible to reduce the interference problems caused by too long lines, especially some important signal lines, such as the clock line. Be sure to place its oscillator very close to the device. When driving multiple devices, the network topology should be decided according to the specific situation.
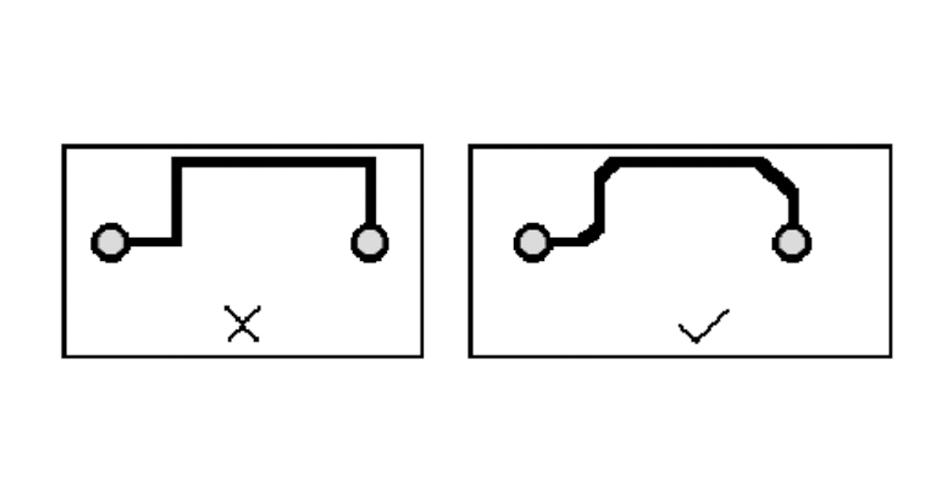
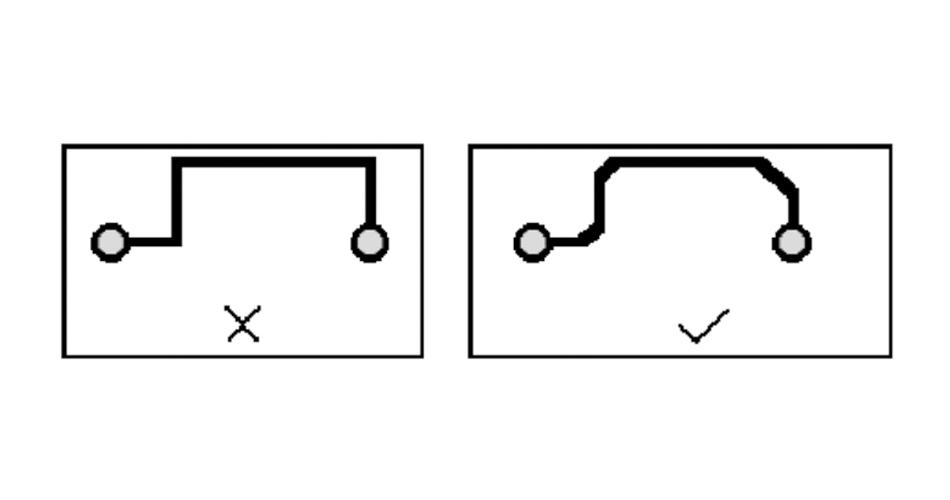
5, chamfering rules.
PCB design should avoid producing sharp corners and right angles, producing unnecessary radiation, while process performance is also bad.
6, device decoupling rules.
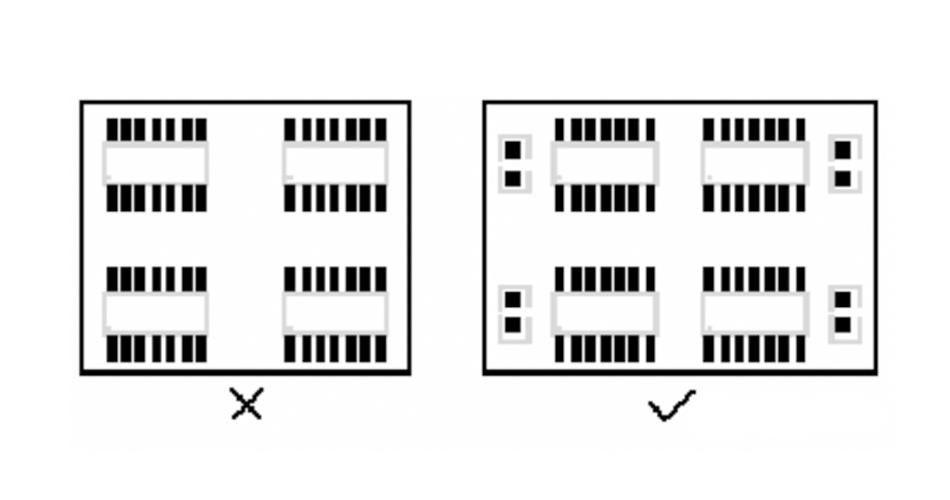
A. Add the necessary decoupling capacitors on the printing plate to filter out the interference signal on the power supply so the power signal is stable. In the multilayer PCB board, the location of the decoupling capacitor is generally less demanding. Still, for a double-layer PCB board, the layout of the decoupling capacitor and the way the power supply is wired will directly affect the entire system’s stability and sometimes even the success or failure of the design.
B. In the double-layer PCB board design, the current should generally be filtered through the filter capacitor and then for the device.
C. In high-speed PCB circuit design, whether the decoupling capacitor can be used correctly is related to the stability of the whole board.
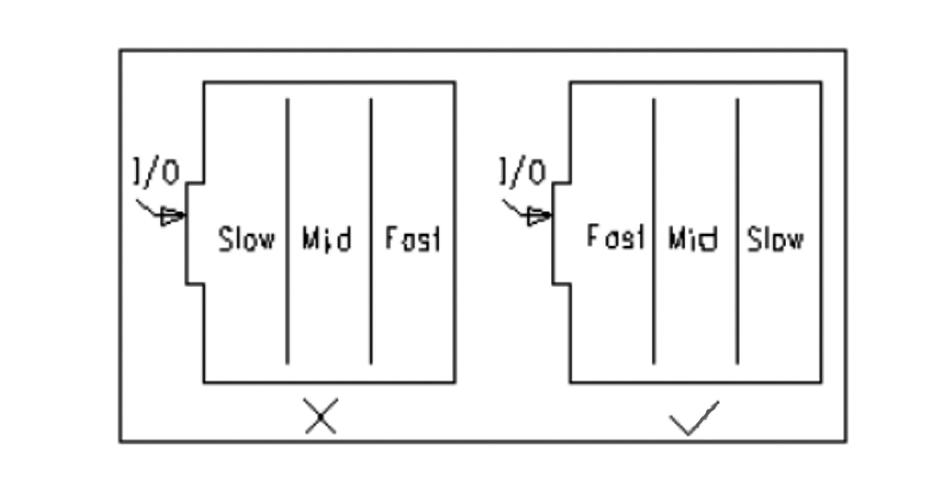
7. PCB device layout partitioning/layering rules.
A. Mainly to prevent mutual interference between modules of different operating frequencies while minimizing the wiring length of the high-frequency part.
B. For mixed circuits, analogue and digital circuits are laid out on both sides of the printed board, respectively, using different wiring layers, the middle with the ground layer isolation.
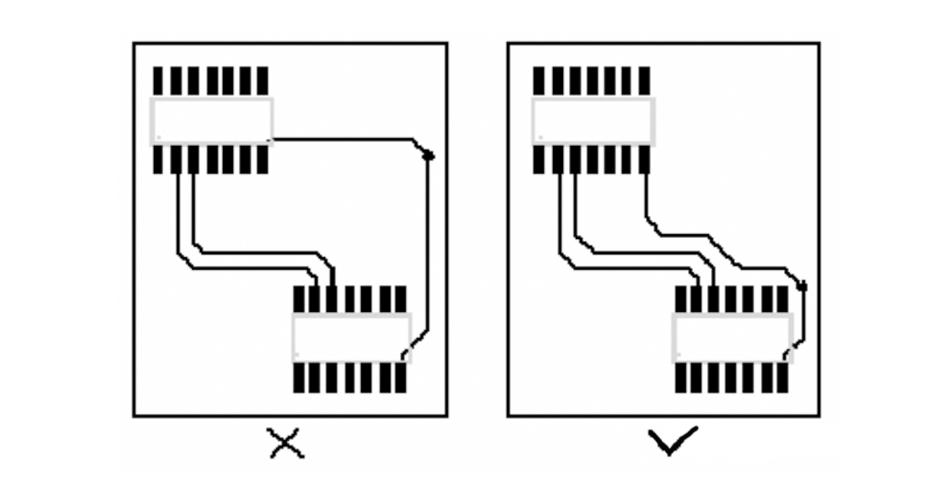
8. Ground loop rules.
Loop minimum rules, that is, the signal line and its loop to form the smallest possible ring area; the smaller the ring area, the less external radiation, and the less interference from the outside world.
9, the integrity of the power and ground layer rules.
For the conductive hole dense area, attention should be paid to avoiding holes in the power and ground layer of the excavation area connected, forming a division of the plane layer, thus destroying the integrity of the plane layer and then leading to the signal line in the ground layer of the loop area increases.
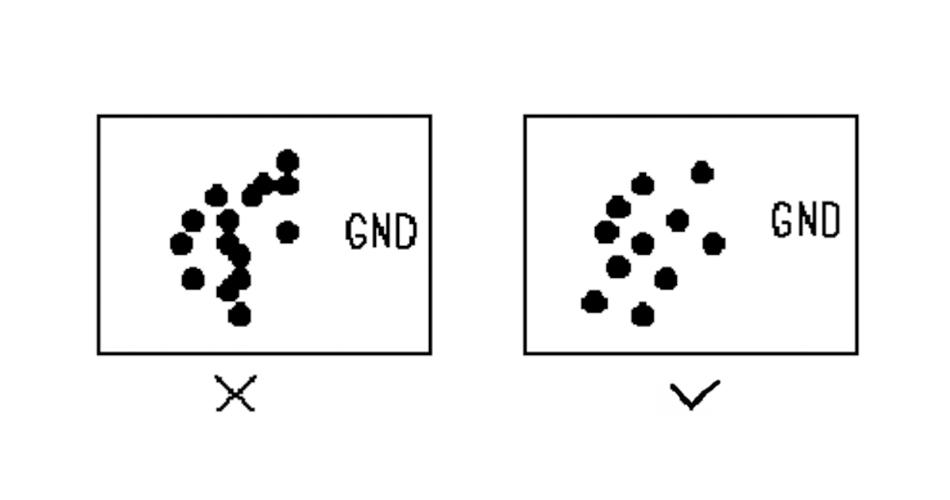
10, 3W rule.
To reduce crosstalk between lines, one should ensure that the line spacing is large enough; when the line centre spacing is less than 3 times the line width, it can maintain that 70% of the electric field does not interfere with each other, known as the 3W rule. If you want to achieve 98% of the electric field that does not interfere with each other, you can use the 10W spacing.
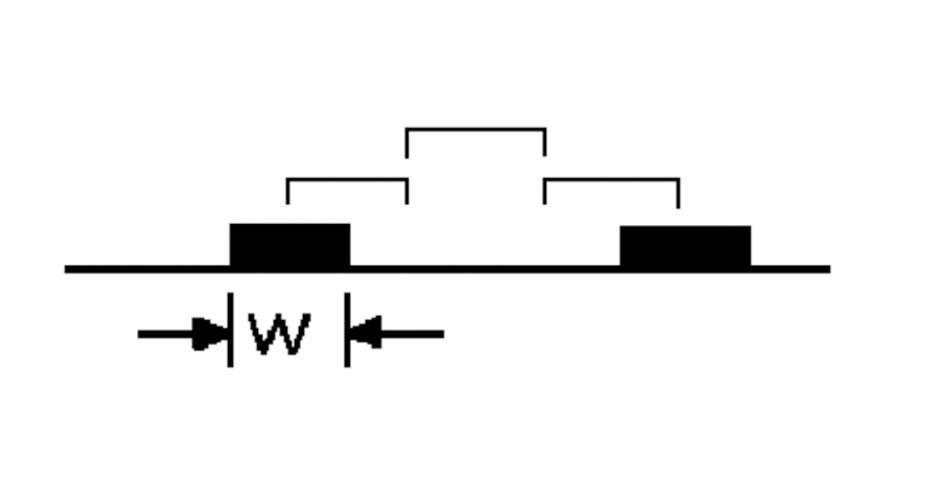
11、Shield protection
Pcb on the corresponding ground loop rule is also to minimize the signal loop area, mostly seen in some of the more important signals, such as clock signals and synchronization signals; for some particularly important, particularly high-frequency signals, should consider the use of copper shaft cable shielding structure design, that is, the line laid up and down left and right with the ground line isolation, but also to consider how to make the shielding ground and the actual ground plane effectively Combination.
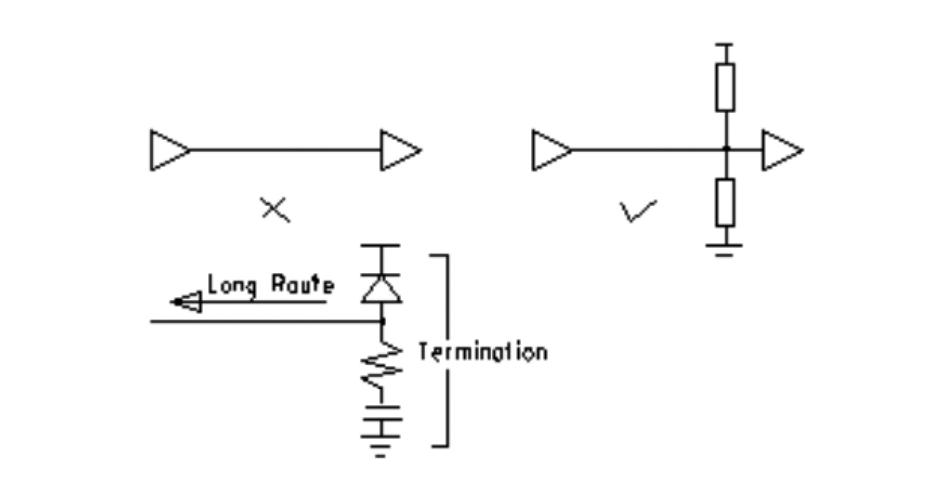
12, alignment termination network rules.
In high-speed PCB digital circuit, when the delay time of the PCB wiring is greater than 1/4 of the signal rise time (or fall time), the PCB wiring that can be seen as a transmission line to ensure that the signal input and output impedance and transmission line impedance correctly matched, you can use a variety of forms of matching methods, the matching method selected with the network connection and wiring topology.
A. For point-to-point (one output for one input) connections, either series matching at the beginning or parallel matching at the end can be chosen. The former is simple and inexpensive but has higher latency. The latter has a good matching effect, but the structure is complicated, and the cost is higher.
B. For point-to-multipoint (one output corresponds to multiple outputs) connection, terminal parallel matching should be selected when the network’s topology is a daisy chain. You can refer to the point-to-point structure when the network is a star structure. Star and daisy chains are the two basic topologies, other structures can be seen as the deformation of the basic structure, and some flexible measures can be taken to match. In practice, considering the cost, power consumption and performance factors, generally do not pursue the exact match, as long as the mismatch caused by the reflection and other interference can be limited to an acceptable range.
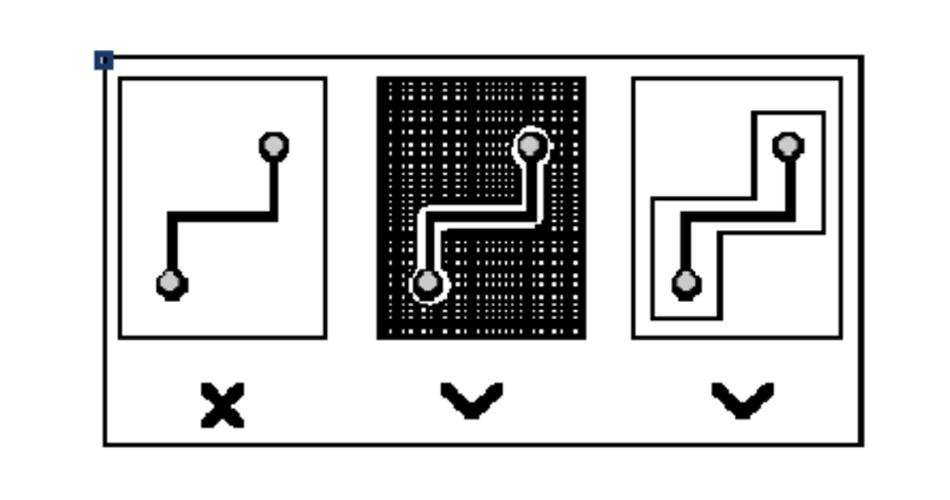
13, pcb alignment closed-loop inspection rules.
Prevent the formation of signal lines in different layers of the self-loop. The multilayer PCB board design is prone to such problems; self-loop will cause radiation interference.
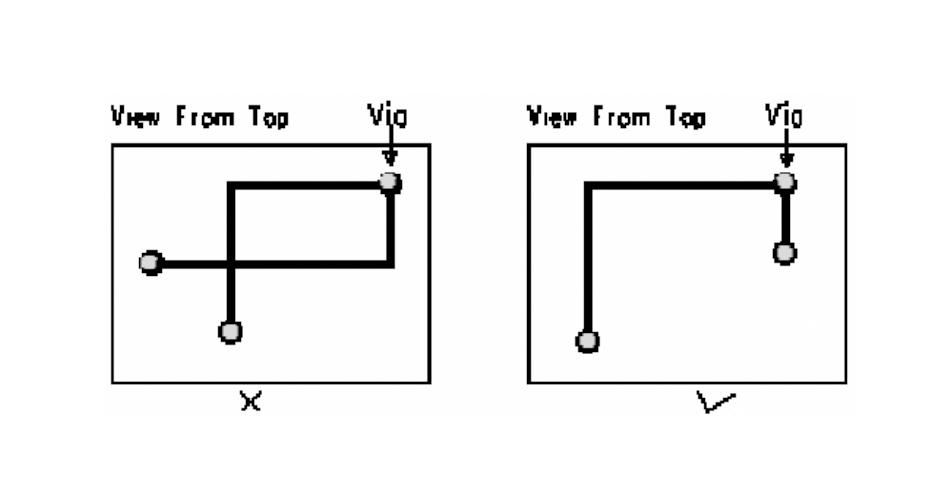
14, PCB alignment of the branch length control rules.
Try to control the length of the branch; the general requirement is Tdelay <= Triose / 20.
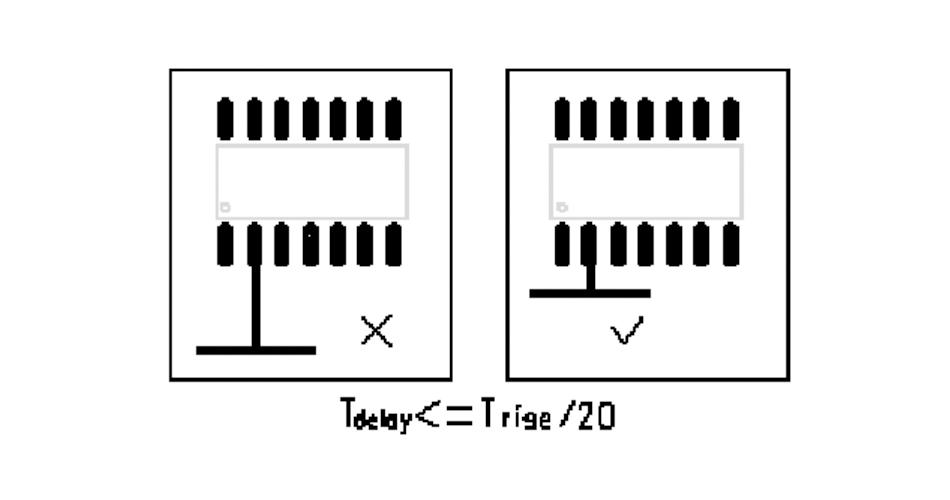
15, PCB alignment of the resonance rules.
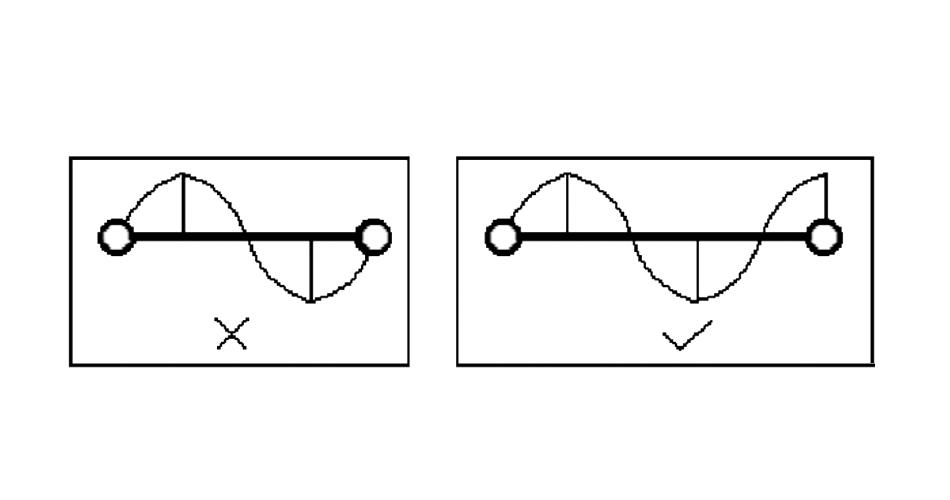
Mainly for the PCB high-frequency signal design, the PCB wiring length shall not be an integer multiple of its wavelength relationship to avoid resonance phenomenon.
16, isolated copper zone control rules.
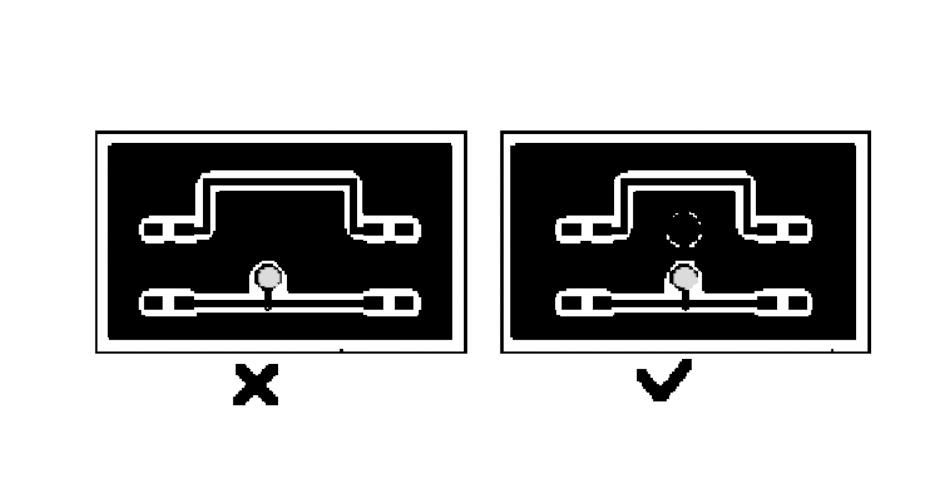
An isolated copper zone will bring some unforeseen problems, so the isolated copper zone and other signals connected to help improve signal quality, usually the isolated copper zone grounded or removed. In the actual production, PCB manufacturers will use some of the vacant parts of the board to add some copper foil, mainly to facilitate the processing of printed circuit boards, but also to prevent the printed circuit board warpage also has a certain role.
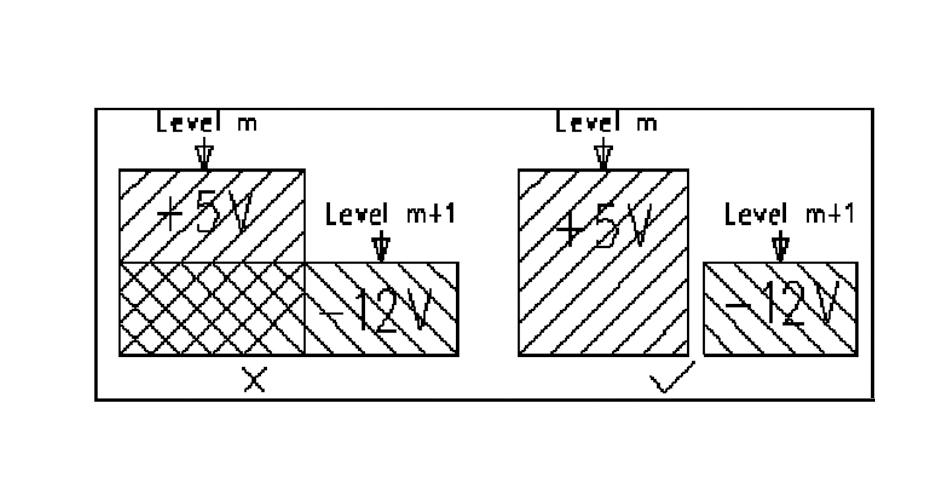
17, overlapping power and ground layer rules.
Different power supply layers in space to avoid overlap. Mainly to reduce the interference between different power supplies, especially some voltage differences between the power supply, the overlap of the power plane must try to avoid the problem, which is difficult to avoid when considering the interval ground layer.
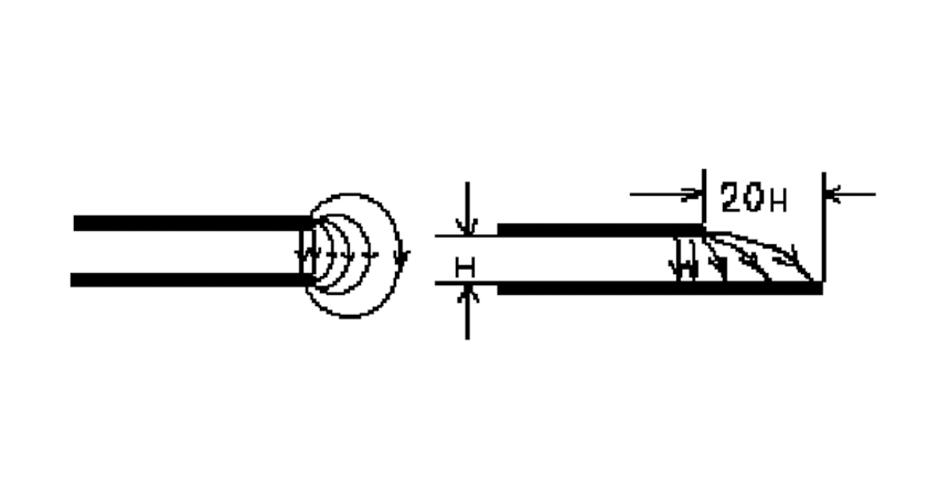
18, 20H rule.
As the electric field between the power supply layer and the ground layer changes, the board’s edge will be radiated outward by electromagnetic interference. Known as the edge effect.
The solution is to shrink the power supply layer so that the electric field is conducted only in the range of the ground layer. To an H (power and ground between the thickness of the medium) as a unit, if the internal shrinkage of 20H can be 70% of the electric field confined to the edge of the ground layer; internal shrinkage of 100H can be 98% of the electric field confined within.
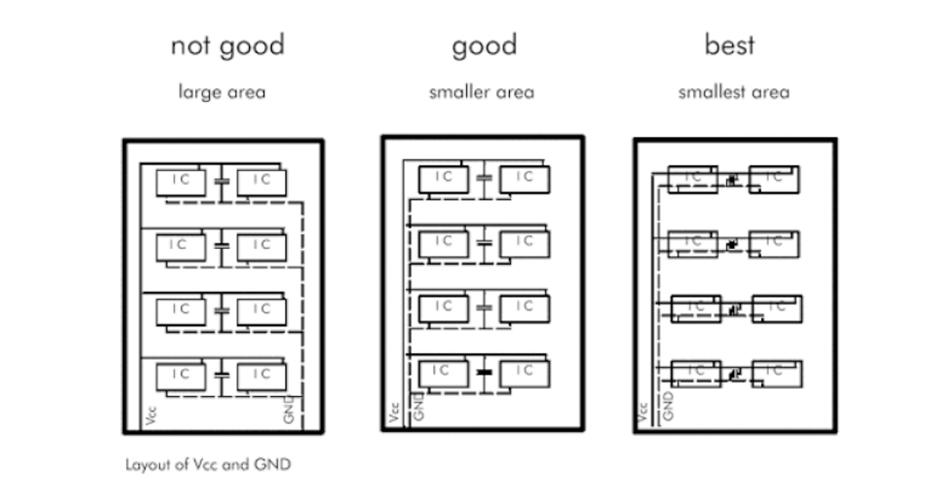
(4) Other
Power lines should be as thick and short as possible for single and double PCB boards. Power and ground line width requirements can be calculated based on a maximum line width of 1mm corresponding to 1A of current; power and ground constitute a loop as small as possible.
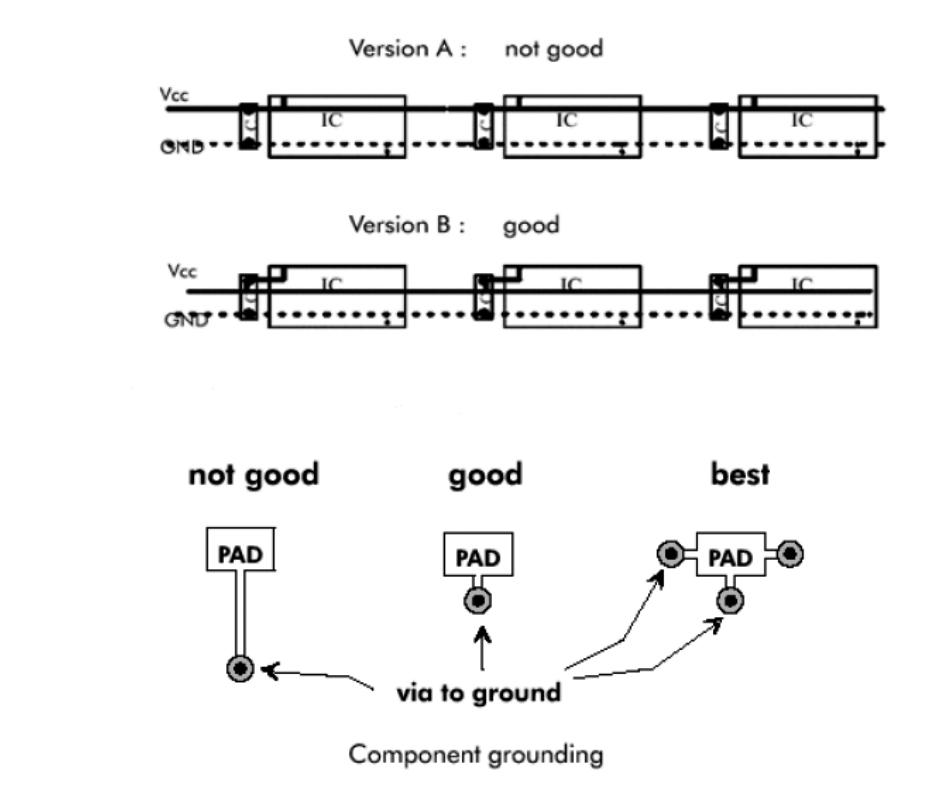
To prevent the coupling noise on the power line from entering the load device directly when the power line is long, the power supply should be decoupled before entering each device. And to prevent them from interfering with each other, the power supply of each load is decoupled independently and filtered before entering the load.
Summary
The above are the practical rules about PCB layout wiring summarized by Anpllopcb’s PCB design engineering in 2022. All the above rules have been effectively verified in practice.
Anpllopcb providing some of the most innovative printed circuit board technologies and highest quality standards in the industry. You can count on us to meet your needs, from the simplest boards to the most complex designs for small quantity and large scale production.